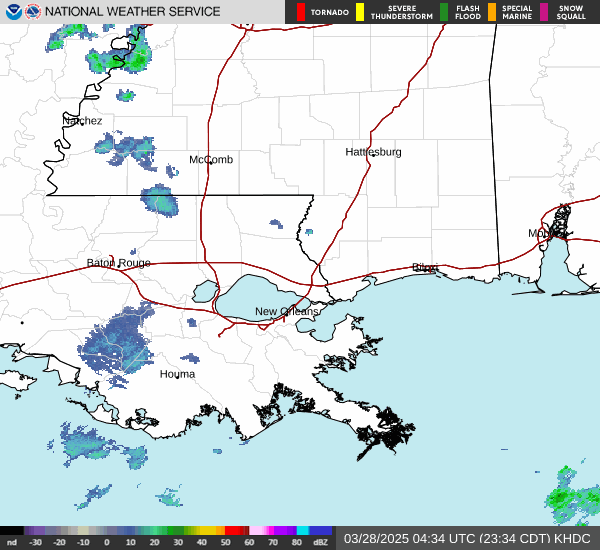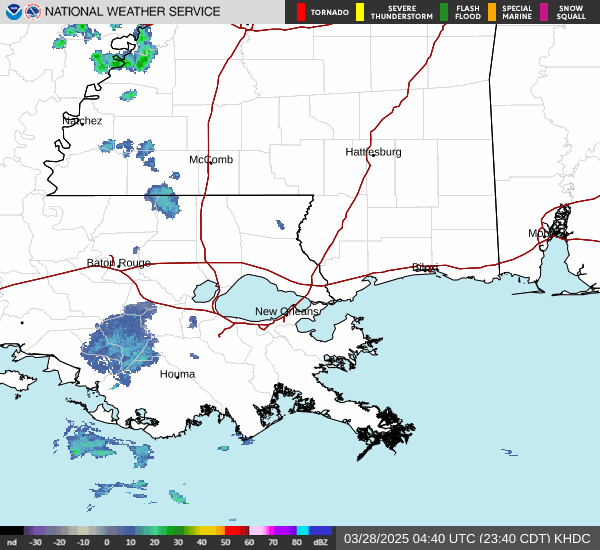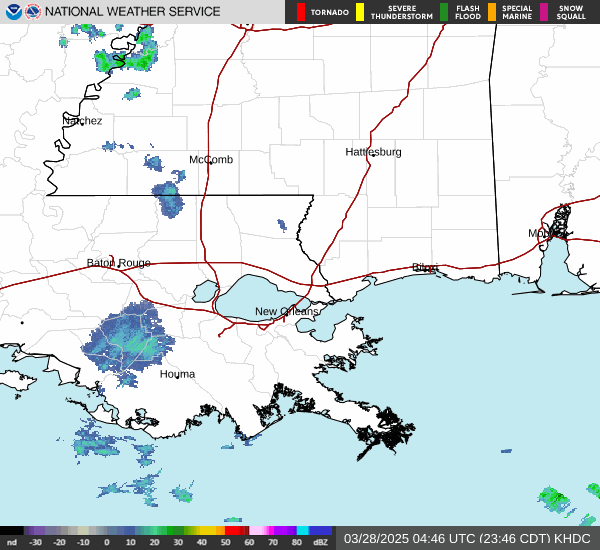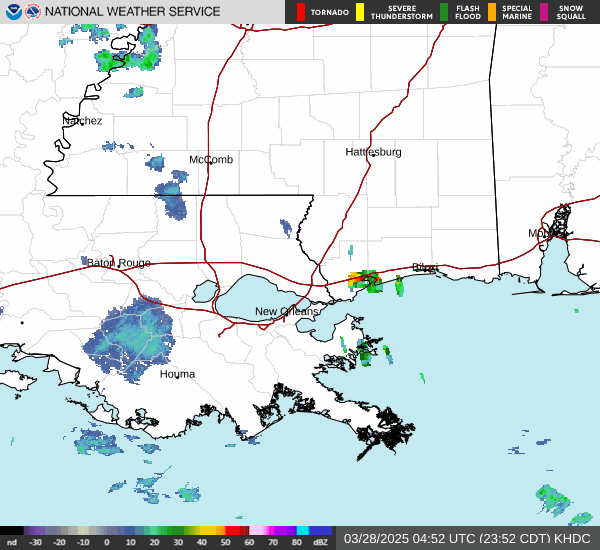
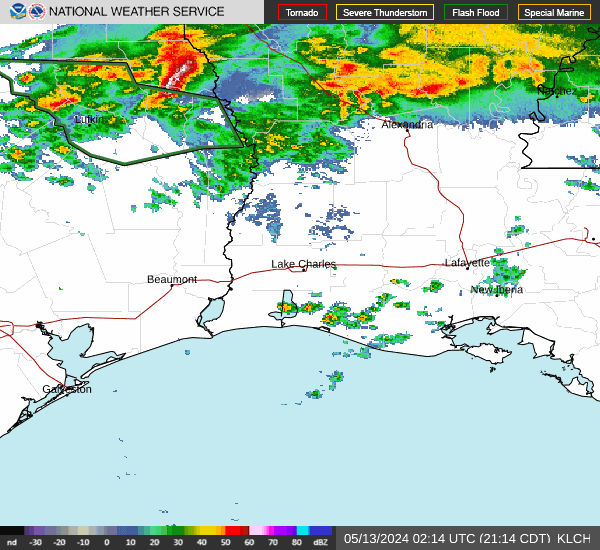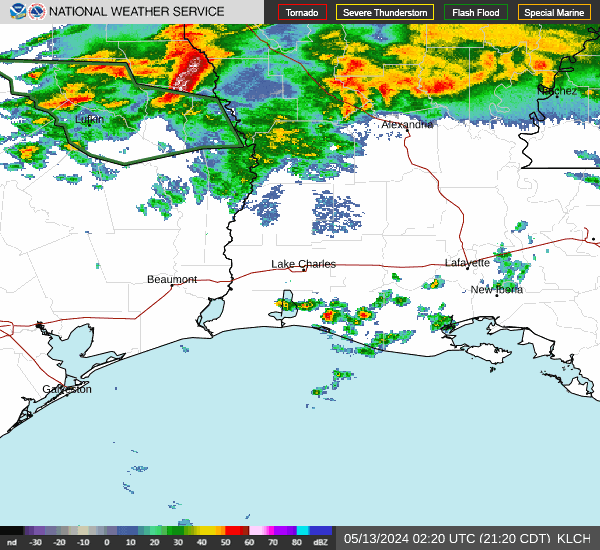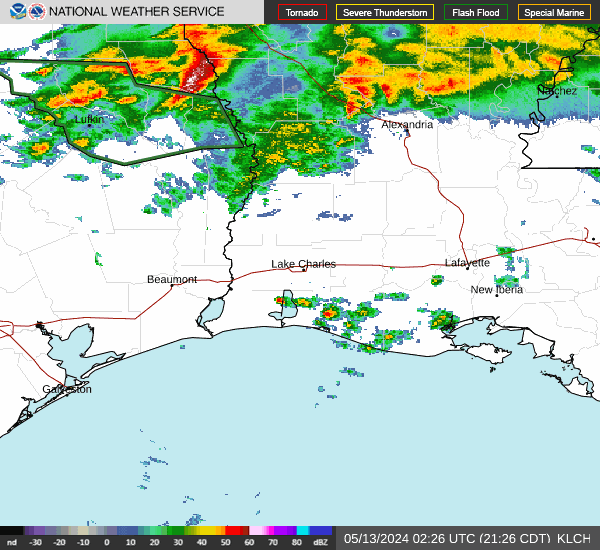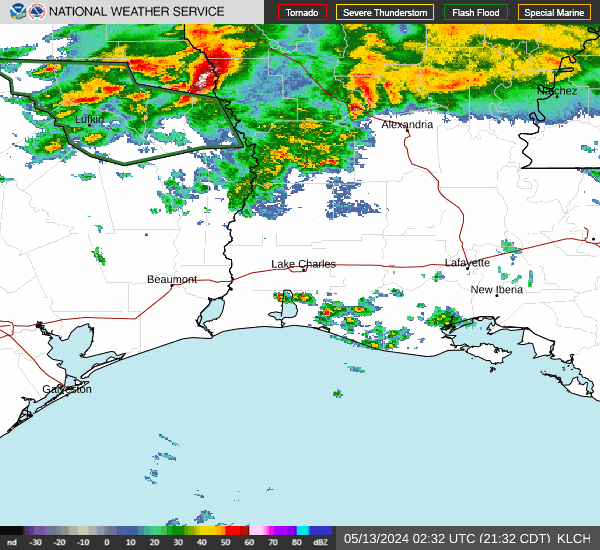
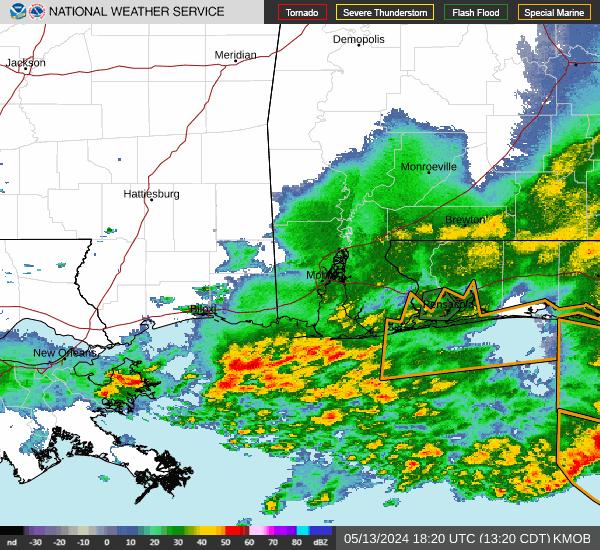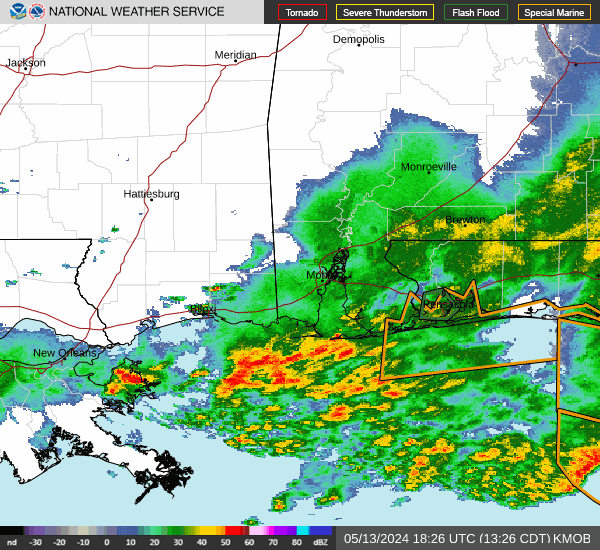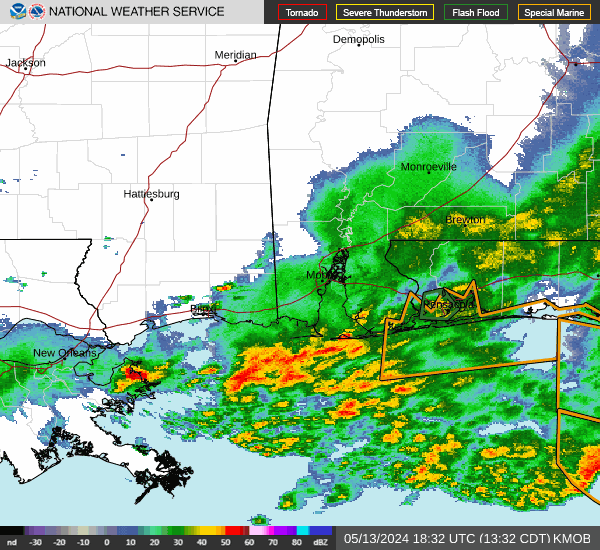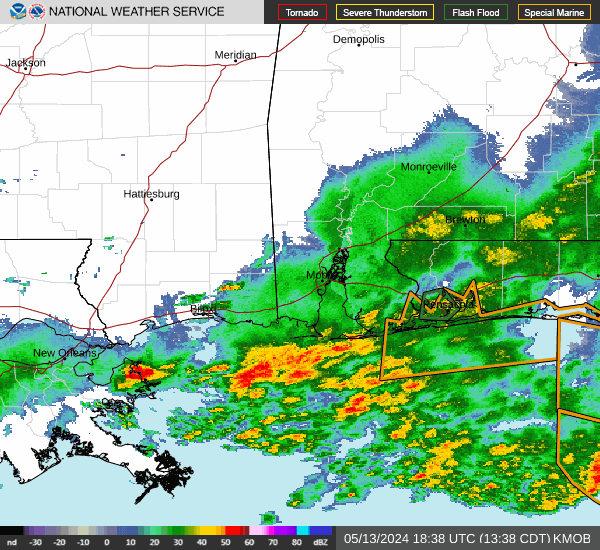
Post by nolasim on Aug 3, 2024 21:52:24 GMT -6

I'll let the NHC address your question. My concern is for rapid intensification; remember the storm in almost the exact location a couple of years ago, was not supposed to be intense but ramped up to about 130 mph?
794
WTNT44 KNHC 040249
TCDAT4
Tropical Storm Debby Discussion Number 7
NWS National Hurricane Center Miami FL AL042024
1100 PM EDT Sat Aug 03 2024
NOAA and Air Force Reserve Hurricane Hunter aircraft have been
investigating Debby during the past few hours and have found that
the winds have increased slightly and the central pressure has
fallen. The NOAA P-3 plane reported SFMR measurements of 35-40 kt
east of the center over the Straits of Florida, and dropsonde data
indicate that the central pressure has fallen to 1003 mb. The
initial intensity is therefore raised to 40 kt.
Debby is gradually turning toward the right and slowing down, and
the initial motion is northwestward, or 320/12 kt. A large mid- to
upper-level trough over the eastern United States has created a
break in the subtropical ridge, which will cause Debby to move
northward over the eastern Gulf of Mexico and approach the
Florida Big Bend region over the next day or two. The track
guidance is in good agreement during this period, and the NHC track
has only been shifted slightly east to account for a slight
relocation of the initial position based on the aircraft data.
After 2-3 days, the steering currents around Debby collapse, and
the cyclone is expected to creep northeastward at less than 5 kt
across northern Florida to near the coasts of Georgia and South
Carolina by day 5. While there is model disagreement on exactly
where Debby will end up on day 5, there is high confidence that the
storm will not be moving very fast, and this slow motion will have
major implications for the associated hazards, particularly heavy
rainfall and flooding.
Low vertical shear and very warm waters (as warm as 32 degrees
Celsius within Apalachee Bay) are likely to support additional
strengthening while Debby approaches the Florida Big Bend. The
intensity guidance has increased a bit on this cycle. Most of the
regional hurricane models are showing Debby reaching hurricane
strength before it reaches the coast, while the
statistical-dynamical SHIPS and LGEM models have increased to the
75-80-kt range. In addition, the Rapid Intensification indices are
showing a 1-in-3 chance of a 45-kt increase in intensity over the
next 36 hours. Based on these model data, the NHC intensity
forecast has been increased to 75 kt in 36 hours, just before the
center of Debby is expected to reach the coast. Weakening is
anticipated after landfall, but Debby's intensity on days 3 through
5 is highly uncertain and is dependent on whether the center moves
over the Atlantic waters and for how long.
WTNT44 KNHC 040249
TCDAT4
Tropical Storm Debby Discussion Number 7
NWS National Hurricane Center Miami FL AL042024
1100 PM EDT Sat Aug 03 2024
NOAA and Air Force Reserve Hurricane Hunter aircraft have been
investigating Debby during the past few hours and have found that
the winds have increased slightly and the central pressure has
fallen. The NOAA P-3 plane reported SFMR measurements of 35-40 kt
east of the center over the Straits of Florida, and dropsonde data
indicate that the central pressure has fallen to 1003 mb. The
initial intensity is therefore raised to 40 kt.
Debby is gradually turning toward the right and slowing down, and
the initial motion is northwestward, or 320/12 kt. A large mid- to
upper-level trough over the eastern United States has created a
break in the subtropical ridge, which will cause Debby to move
northward over the eastern Gulf of Mexico and approach the
Florida Big Bend region over the next day or two. The track
guidance is in good agreement during this period, and the NHC track
has only been shifted slightly east to account for a slight
relocation of the initial position based on the aircraft data.
After 2-3 days, the steering currents around Debby collapse, and
the cyclone is expected to creep northeastward at less than 5 kt
across northern Florida to near the coasts of Georgia and South
Carolina by day 5. While there is model disagreement on exactly
where Debby will end up on day 5, there is high confidence that the
storm will not be moving very fast, and this slow motion will have
major implications for the associated hazards, particularly heavy
rainfall and flooding.
Low vertical shear and very warm waters (as warm as 32 degrees
Celsius within Apalachee Bay) are likely to support additional
strengthening while Debby approaches the Florida Big Bend. The
intensity guidance has increased a bit on this cycle. Most of the
regional hurricane models are showing Debby reaching hurricane
strength before it reaches the coast, while the
statistical-dynamical SHIPS and LGEM models have increased to the
75-80-kt range. In addition, the Rapid Intensification indices are
showing a 1-in-3 chance of a 45-kt increase in intensity over the
next 36 hours. Based on these model data, the NHC intensity
forecast has been increased to 75 kt in 36 hours, just before the
center of Debby is expected to reach the coast. Weakening is
anticipated after landfall, but Debby's intensity on days 3 through
5 is highly uncertain and is dependent on whether the center moves
over the Atlantic waters and for how long.